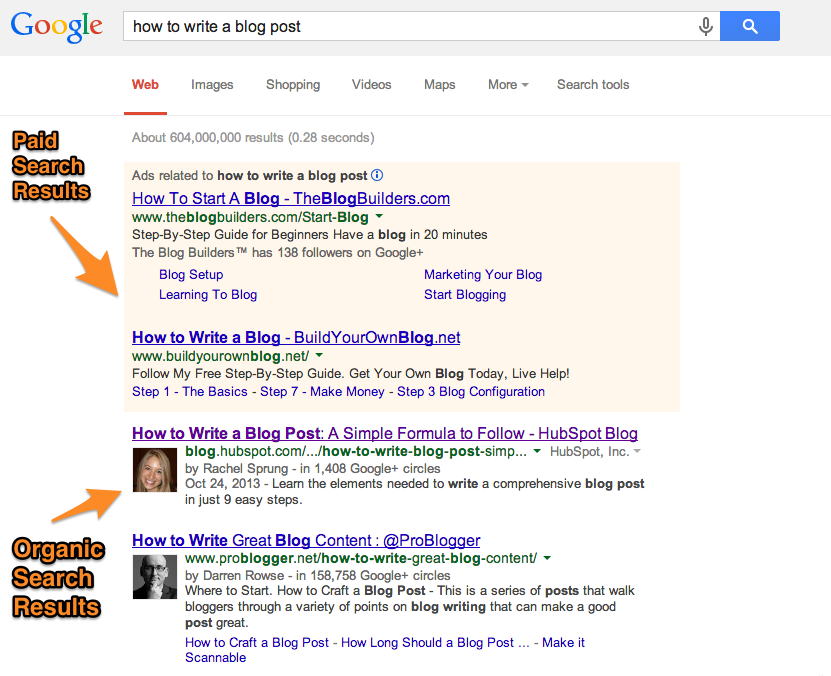
Are you looking for some love… from Google? Other than buying paid traffic through their AdWords program, the best way to get more traffic from them is through search engine optimization. But before you start optimizing your site, the first thing you should do is sign up for Google Webmaster Tools (GWT).
GWT is a free toolset provided by Google that helps you first understand what’s going on with your website. This way you make decisions based off of data instead of going in blindly.
Here is how GWT works.
Adding your website
add a website to google webmaster tools
The first thing you need to do after you login to GWT (it’s free to sign up) is to add your website.
After you add your website you’ll have to verify that you actually own the website. You can do this through four ways:
- Add a DNS record to your domain’s configuration – You can use this option if you can sign in to your domain registrar or hosting provider and add a new DNS record.
- Add a meta tag to your site's homepage – You can choose this option if you can edit your site’s HTML.
- Upload an HTML file to your server – You can choose this option if you can upload new files to your site.
- Link your Google Analytics account to GWT – You can use this option if your site already has a Google Analytics tracking code that uses the asynchronous snippet. You must be an administrator on the analytics account for this to work.
Dashboard
google webmaster tools dashboard
Once your site is verified you’ll start seeing data on your website. Sometimes it can take a few hours before you see any data, but it’ll start rolling in.
The dashboard gives you a rough overview of everything from what keywords you are ranking for to how much traffic you are getting. In addition to that, you’ll see if the Google bot is experiencing any crawl errors when going to your website, the number of sites linking to yours, and how many pages Google has indexed.
Site Configuration
Just like everything else, Google isn’t perfect. So configuring your site can help them do a better job of ranking your website. When configuring there are a few areas that you should be familiar with:
Sitemaps
google webmaster tools sitemaps
Submitting a sitemap will help Google determine what pages you have on your website so they can index them. If you don’t submit a sitemap they may not index all of the pages on your website, which means you won’t get as much traffic.
Sitemaps have to be submitted in an XML format and they can’t contain more than 50,000 URLs or be larger than 10 megs. If you exceed any of those limits, you need to split up your sitemap into multiple files and then submit them.
If you aren’t technical, you can go to XML Sitemaps to create a sitemap. All you have to do is enter your URL of your homepage and click “start”.
Once your sitemaps have been uploaded, Google will tell you how many of your URLs are being indexed. Don’t worry, it is common for them to not index all of your web pages. But your goal should still be to get as many pages indexed as possible.
Typically if pages aren’t being indexed it’s because the content on those pages isn't unique, the title tags and meta descriptions are generic, and not enough websites are linking to your internal pages.
Crawler access
google webmaster tools crawler access
There will be some pages on your website that you just don’t want Google to index. This could be private login areas, RSS feeds, or crucial data that you don’t want people accessing.
By creating a robots.txt file you can block not just Google, but all search engines from accessing web pages that you don’t want them to get their hands on. However, for highly sensitive areas of your website you may want to consider password protecting all relevant directories.
Through the robots.txt generator and tester, not only will you be able to create a robots.txt file, but you will be able to see if it is done correctly before you upload it to your server. It’s wise to do because the last thing you want to do is make a mistake and tell them not to index your whole website.
And if you accidentally mess up and find Google indexing pages that you don’t want them to index, you can request them to remove it from this section.
Sitelinks
google webmaster tools sitelinks
Sitelinks are links to a site’s interior pages displayed on a Google search results page. Not all sites have sitelinks, but as you grow in popularity you’ll naturally get them. Google generates these links automatically, but you can remove sitelinks you don’t want.
Through this section, you can somewhat control what sitelinks show up when someone searches for your website. The reason you can’t fully control what pages show up here is that you can only block which pages you don’t want to appear, and you can’t pick which pages you want to appear.
Change of address
google webmaster tools change of address
If you are looking to change the URL of your website, you better let Google know or else your traffic is going to decrease.
You can tell them through 4 easy steps:
Setup the new site – You have to get the new domain up and running. Make sure all your content is available for the public to see.
Redirect the old traffic – A 301 permanent redirect tells users and search engines that your site has permanently moved.
Add your new site to GWT – Make sure you also verify your new website.
Tell GWT your new domain – In the change of address section, you can select the new domain name of your website.
Settings
google webmaster tools settings
If your target audience is someone in a specific country, then you can select this option in GWT. For example, if my target customer for KISSmetrics lives in the United States, I would then tell GWT that my target audience lives in the United States.
In addition to that, you can select a preferred domain name. This is going to be http://yourdomain.com or http://www.yourdomain.com. Either one works, you just have to select which variation you prefer. The reason for picking one is that people may link to both versions of your domain and by selecting one Google will combine the links, which will help your rankings.
The last setting you should be worried about is crawl rate. If you feel that the Google bot needs to be crawling your website more often and faster then you can tell them to do so. Or you can just let them pick the crawl setting for your website. (this is typically the best option because if they crawl your website too often it can cause too much bot traffic going to your server and increase your hosting costs)
Your website on the web
Have you ever wondered how Google looks at your website? After all, it’s a search engine and not a human… so naturally it won’t be able to look at a website in the same way you do.
But luckily for you, through GWT you can see how Google views your website.
Search queries
google webmaster tools search queries
Not only is it important to go after keywords that have high search volume, but it is important to make sure that you have a good click-through rate.
By monitoring the search queries page, you can work on improving your click-through rate so that people are more likely to click on your listing when they search. Typically you can do this by making your title tag and meta description more attractive as that is what people read before clicking through to your site.
Links to your website
google webmaster tools links to your site
The best way to increase your rankings on Google is to get more sites to link to you. Usually, this happens naturally if your website is providing valuable information to potential customers.
A good way to monitor your link growth is to continually monitor this area in GWT. In addition to that, make sure you monitor which pages people are linking to.
If your links aren’t growing fast enough consider writing relevant linkbait that could be submitted throughout the social web. Getting on the homepage of Digg.com can drive thousands of new links to your site.
Keywords
google webmaster tools keywords
You may have a good idea of what keywords you want to rank for, but that may not be consistent with what Google is ranking you for. Under the keywords section, you can see what keywords your website is the most related to.
You can also see what variations of each keyword that are also relevant to your website. For example, some people misspell keywords and you can find out which misspellings your website is most relevant for.
And if those aren’t the keywords you care to rank for, you can then use that data to adjust the content on your website.
Internal links
Google Webmaster Tools Internal Links
Linking your web pages together is a great way to get more Google love. For example, if you want your about page to rank for your company name make sure you link to it multiple times.
If you don’t link to your internal pages, they will not get as much PageRank and they won’t place as well in the search listings.
In addition to that, this data will also help you determine which pages Google feels is the most important. For example, if you look at the image above you’ll see that website owner felt that their about pages was one of the most important pages on their website. So naturally, Google felt that as well.
Subscriber stats
google webmaster tools subscriber stats
If you have a blog, this area of GWT will be useful for you. If you don’t, it won’t.
Under the subscriber stats section, you can see which of your blog posts are the most subscribed to by Google’s feed reader. You can then take that data and write more posts that are similar to your popular ones. And of course, you can stop writing blog posts similar to the ones that no one subscribed to, as readers probably didn’t enjoy them as much.
On a side note, if you want to track your RSS growth, you can also check out Feedburner, which will allow you to track how popular your feed is.
Diagnostics
Websites are made by humans, so don’t expect them to be perfect. Your code may be a bit messed up, and even worse, your website may contain malware.
Through the diagnostics section, you can figure out what’s wrong with your site and how you can fix it.
Malware
google webmaster tools malware
If you have malware on your server, you should see a message here. If you don’t, GWT won’t show you much.
The reason it is important to not have malware on your server is that Google tries not to rank infected sites high because if someone goes to an infected site, their computer may get infected. If you do happen to have malware, make sure you clean it up.
Crawl errors
google webmaster tools crawl errors
The crawl errors section will show you if there any problems that relate to your site on the web or on a mobile phone. The most common error that you’ll see is a 404 error, which means Google’s bot can’t find that page.
The most common reason that you’ll see 404 errors is that other websites sometimes link to pages that don’t exist on your website or used to exist.
What you need to do is get a list of all of the websites that are linking to dead pages on your site and hit them up. When emailing them, ask them if they can change that link to a valid page.
Or if you see a lot of people linking to a dead page on your site, you can always 301 redirect that old URL to the new URL.
Crawl stats
google webmaster tools crawl stats
If you have thousands of pages on your site, then you should expect Google to crawl most of these pages on a daily or weekly basis. If they aren’t, then something is wrong.
Through the graphs and data tables that GWT provides, you should be able to get a good sense if they are crawling enough pages on your website. If they aren’t, consider adjusting the crawl rate under the settings tab.
HTML suggestions
google webmaster tools HTML suggestions
When Googlebot crawls your site, it may find some issues with your content. These issues won’t prevent your site from appearing in Google search results, but addressing them may help boost your traffic.
The most common problem is related to title tags and meta descriptions. If every page on your site has unique and detailed title tags and meta descriptions, you should be fine. At the same time, you also have to make sure your title tags aren’t too short or too long.
And if that isn’t the case, then you can go through the URLs that GWT tells you they have an issue with and fix it.
Labs
GWT regularly tests new features out. The easiest way to find out about these new features is to go through the lab's sections.
Fetch as Googlebot
google webmaster tools fetch as Googlebot
With Fetch as Googlebot, you can see exactly how a page appears to Google. All you have to do is type in a URL and GWT will tell if they could successful see it or not.
There currently isn’t a ton of data that GWT is showing in this area, but I expect this to change in the future.
Sidewiki
google webmaster tools Sidewiki
If you’re a webmaster, you can leave a special Sidewiki entry on pages of your site. You can choose to leave a master entry for the whole site, or create page specific entries to engage your visitors.
All you have to do is:
If you’ve successfully validated your account in GWT, you will see an option to write as the page owner.
Select the “Write as the page owner” checkbox in the entry form. If you’d like to leave a master entry across the whole site, also select the “Show this page owner entry on all pages…” checkbox.
Click Publish.
Site performance
google webmaster tools site performance
Your website’s load time is one of the most important things you should be monitoring. Every month you should be making sure you improve this number because if your website is too slow your Google traffic may drop.
Numerous website owners have seen a positive increase in their traffic by improving their website load time.
If you aren’t sure how fast your website should load, don’t worry. Google will tell you if your website is too slow or quick enough.
Video sitemaps
google webmaster tools video sitemaps
If you have a video on your site, you want to make sure you include those raw video files in your sitemap. This way, Google can index them as they may not be able to find them otherwise.
This will help ensure that your videos are getting the traffic they deserve from Google video search.
If you are trying to create a video sitemap, this page should explain how to do so.
Conclusion
GWT is a useful tool that’s free. If you aren’t making use of it, you should start doing so now. The reason it’s worth using is that it will help guide you and tell you what to do if you want to improve your Google traffic.